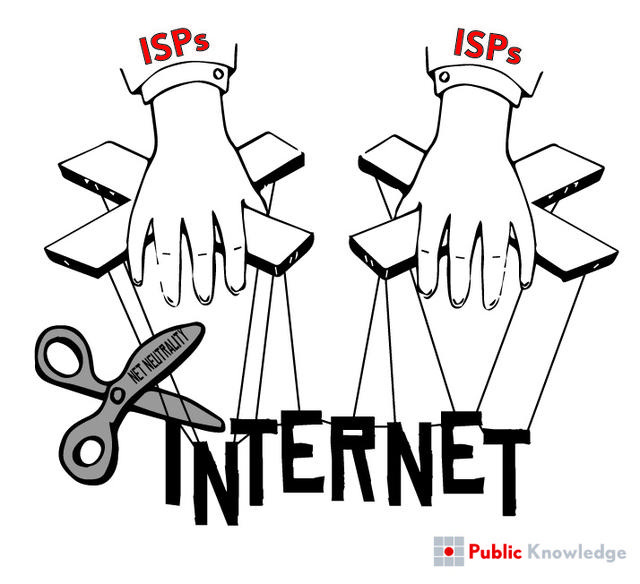
Expanding on The Switch’s 5 things that neither side of the broadband debate wants to admit.
 Over at The Switch today, Timothy B. Lee offered his list of 5 things neither side of the broadband debate wants to admit. His list strikes me as mostly reasonable, although I think that you could find at least one side of the debate to endorse most of them. In any case, I wanted to take a moment to add a bit of color to the list, to try and give you a sense of how we think about some of these things. Here are Lee’s things, followed by a bit of commentary.
Over at The Switch today, Timothy B. Lee offered his list of 5 things neither side of the broadband debate wants to admit. His list strikes me as mostly reasonable, although I think that you could find at least one side of the debate to endorse most of them. In any case, I wanted to take a moment to add a bit of color to the list, to try and give you a sense of how we think about some of these things. Here are Lee’s things, followed by a bit of commentary.
1. American wireless service is working pretty well.
Especially when compared to the wired broadband market, this statement is fairly accurate. We have four nationwide carriers and some decisions (like offering earlier upgrades) by one carrier clearly push the other carriers to match.
I would add two additional data points to that statement, however. Lee mentions that, in 2007, there was a great deal of concern about wireless carrier control over mobile software. He then points out that Apple’s decision to open up the iPhone to third party developers rendered the concern “obsolete.” While no one would argue that the state of mobile software has improved massively since 2007, I don’t know that I would go so far as to say that concerns about network operator control are necessarily obsolete. Even today we have carriers preventing some types of services from running on phones connected to their network. And carriers are still working hard to prevent you from unlocking the phone that you own from their network.
Moreover, this state of working pretty well was not necessarily the wireless industry’s destiny. As we have pointed out before, the FCC’s decisions to reject mergers and signal that it would support four competitive nationwide carriers have done a great deal to preserve the level of competition we have today. That does not undercut Lee’s point, but it is worth keeping in mind.
2. We’re falling behind on residential broadband.
It won’t come as a surprise that we’re quite willing to admit that one. The theory of facilities-based competition between telephone companies, cable companies, satellite providers, and even power companies has turned out to be weak in practice. While, as Lee points out, some like to point to DSL or satellite as viable competitors, the reality is that they are not. Coming to terms with this state of affairs would bring us a huge way towards developing rational broadband policies.
3. We desperately need more broadband experimentation.
Again, we’ll admit this one too. Our allies at the Institute for Local Self Reliance do fantastic work trying to help localities build their own local networks and push back against statewide bans on such experimentation.
On the flip side, we get wary that “experimentation” can also be interpreted as an excuse for existing ISPs to inject themselves into the value chain through data caps or special priority fast lanes. In a world with limited broadband competition (see point 2), there are few market protections for consumers with ISPs who want to experiment by exploiting their control over customers. This does not mean that ISPs should not be prevented from experimenting. But these types of concerns should be kept in mind when thinking about those experiments.
4. Discrimination concerns are mostly about video streaming.
This strikes me as sort of, but not totally, true. Video streaming gets a lot of attention these days. In part, this is because video is one of the most data-intensive applications that most people will use on a regular basis. Therefore it is an easy way for people to understand more general concerns about discrimination.
Of course, there are also some video-specific discrimination concerns. As Lee points out, most Americans connect to the internet through their cable provider. And the role of competitor to online video and keeper of a key ingredient to the success of online video can create some problems.
But video is not the only potential victim of discrimination. The internet moves quickly and new applications can seemingly emerge over night. While I don’t know what it is, it is not hard to imagine a whole new generation of data-intensive applications that could be just as vulnerable to discrimination as online video is today. So while the discussion is about video today, that doesn’t mean that it will be about video tomorrow.
5. “Network neutrality” probably isn’t the answer.
Again, this is one that I agree with in part and disagree with in part. I agree that network neutrality is not the only answer. One of the reasons that we started WhatIsNetNeutrality.orgwas to remind people that net neutrality is actually a fairly specific thing, and that “net neutrality violation” was not just synonymous with “a bad thing happening on the internet.” There are going to be a number of developments that raise concerns about internet access but have nothing to do with net neutrality.
That being said, net neutrality is an answer to some of those concerns. Net neutrality rules helped to resolve the dispute surrounding AT&T’s decision to block the Facetime app for some of its customers. Perhaps more tellingly, last week Verizon explained that the FCC’s net neutrality rules were the only thing preventing it from trying to force some websites and services to pay to get special access to its customers. I’m pretty confident that the existence of net neutrality are at least part of the reason that problematic behavior has migrated to other places in the network.
Those quibbles aside, Lee’s five things feel like they are in the right neighborhood to me. Perhaps most importantly, they serve as an important reminder to move beyond that state of play in 2003. We at Public Knowledge work hard to keep abreast of the evolving technical and business reality of the internet and to adjust our advocacy accordingly. But it never hurts to get another reminder that things evolve and that we need to as well.
Original image by Flickr user SweetKaran.

 Earlier this week, the
Earlier this week, the Yesterday’s
Yesterday’s